Pandas is arguably the most important Python package for data science. Not only does it give you lots of methods and functions that make working with data easier, but it has been optimized for speed which gives you a significant advantage compared with working with numeric data using Python's built-in functions.
It's common when first learning pandas to have trouble remembering all the functions and methods that you need, and while at Dataquest we advocate getting used to consulting the pandas documentation, sometimes it's nice to have a handy reference, so we've put together this cheat sheet to help you out!
If you're interested in learning pandas, you can consult our two-part pandas tutorial blog post, or you can signup for free and start learning pandas through our interactive pandas for data science course.
Python for Data Science Cheat Sheets. Python is one of the most widely used programming languages in the data science field.Python has many packages and libraries that are specifically tailored for certain functions, including pandas, NumPy, scikit-learn, Matplotlib, and SciPy.The most appealing quality of Python is that anyone who wants to learn it, even beginners, can do so quickly and easily. This cheat sheet on data exploration operation in Python using Pandas is your go-to resource to know each step involved in data exploration. You will find cheat codes for reading & writing data, preview of dataframes, rename columns of dataframe, aggregate the data, etc. Python - Pandas Cheat Sheet by Pitbull (aggialavura) via cheatography.com/83764/cs/19829/ TO START import numpy as np import pandas as pd SERIES (similar to numpy array) pd.Series(data = list) create. Python notebook using data from Kernel Files 21,941 views 1y ago programming. Copy and Edit 281. Version 13 of 13. Table of Contents Data Structures Numpy Pandas. Input (1) Output Execution Info Log Comments (14) Cell link copied. This Notebook has been released under the Apache 2.0 open source license. Much like the other cheat sheets, there is comprehensive coverage of the pandas basic in here. So, that includes filtering, sorting, importing, exploring, and combining DataFrames. However, where this Cheat Sheet differs is that it finishes off with an excellent section on scikit-learn, Python's machine learning library.
Key and Imports
In this cheat sheet, we use the following shorthand:
Pandas Python Cheat Sheet
df | Any pandas DataFrame object |
s | Any pandas Series object |
You'll also need to perform the following imports to get started:
Importing Data
pd.read_csv(filename) | From a CSV file |
pd.read_table(filename) | From a delimited text file (like TSV) |
pd.read_excel(filename) | From an Excel file |
pd.read_sql(query, connection_object) | Read from a SQL table/database |
pd.read_json(json_string) | Read from a JSON formatted string, URL or file. |
pd.read_html(url) | Parses an html URL, string or file and extracts tables to a list of dataframes |
pd.read_clipboard() | Takes the contents of your clipboard and passes it to read_table() |
pd.DataFrame(dict) | From a dict, keys for columns names, values for data as lists |
Exporting Data
df.to_csv(filename) | Write to a CSV file |
df.to_excel(filename) | Write to an Excel file |
df.to_sql(table_name, connection_object) | Write to a SQL table |
df.to_json(filename) | Write to a file in JSON format |
Create Test Objects
Useful for testing code segements
pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(20,5)) | 5 columns and 20 rows of random floats |
pd.Series(my_list) | Create a series from an iterable my_list |
df.index = pd.date_range('1900/1/30', periods=df.shape[0]) | Add a date index |
Viewing/Inspecting Data
df.head(n) | First n rows of the DataFrame |
df.tail(n) | Last n rows of the DataFrame |
df.shape() | Number of rows and columns |
df.info() | Index, Datatype and Memory information |
df.describe() | Summary statistics for numerical columns |
s.value_counts(dropna=False) | View unique values and counts |
df.apply(pd.Series.value_counts) | Unique values and counts for all columns |
Selection
df[col] | Return column with label col as Series |
df[[col1, col2]] | Return Columns as a new DataFrame |
s.iloc[0] | Selection by position |
s.loc['index_one'] | Selection by index |
df.iloc[0,:] | First row |
df.iloc[0,0] | First element of first column |
Data Cleaning
df.columns = ['a','b','c'] | Rename columns |
pd.isnull() | Checks for null Values, Returns Boolean Arrray |
pd.notnull() | Opposite of pd.isnull() |
df.dropna() | Drop all rows that contain null values |
df.dropna(axis=1) | Drop all columns that contain null values |
df.dropna(axis=1,thresh=n) | Drop all rows have have less than n non null values |
df.fillna(x) | Replace all null values with x |
s.fillna(s.mean()) | Replace all null values with the mean (mean can be replaced with almost any function from the statistics section) |
s.astype(float) | Convert the datatype of the series to float |
s.replace(1,'one') | Replace all values equal to 1 with 'one' |
s.replace([1,3],['one','three']) | Replace all 1 with 'one' and 3 with 'three' |
df.rename(columns=lambda x: x + 1) | Mass renaming of columns |
df.rename(columns={'old_name': 'new_ name'}) | Selective renaming |
df.set_index('column_one') | Change the index |
df.rename(index=lambda x: x + 1) | Mass renaming of index |
Filter, Sort & Groupby
df[df[col] > 0.5] | Rows where the col column is greater than 0.5 |
df[(df[col] > 0.5) & (1.7)] | Rows where 0.7 > col > 0.5 |
df.sort_values(col1) | Sort values by col1 in ascending order |
df.sort_values(col2,ascending=False) | Sort values by col2 in descending order |
df.sort_values([col1,ascending=[True,False]) | Sort values by col1 in ascending order then col2 in descending order |
df.groupby(col) | Return a groupby object for values from one column |
df.groupby([col1,col2]) | Return groupby object for values from multiple columns |
df.groupby(col1)[col2] | Return the mean of the values in col2, grouped by the values in col1 (mean can be replaced with almost any function from the statistics section) |
df.pivot_table(index=col1,values=[col2,col3],aggfunc=max) | Create a pivot table that groups by col1 and calculates the mean of col2 and col3 |
df.groupby(col1).agg(np.mean) | Find the average across all columns for every unique col1 group |
data.apply(np.mean) | Apply a function across each column |
data.apply(np.max,axis=1) | Apply a function across each row |
Join/Comine
df1.append(df2) | Add the rows in df1 to the end of df2 (columns should be identical) |
df.concat([df1, df2],axis=1) | Add the columns in df1 to the end of df2 (rows should be identical) |
df1.join(df2,on=col1,how='inner') | SQL-style join the columns in df1 with the columns on df2 where the rows for col have identical values. how can be one of 'left', 'right', 'outer', 'inner' |

Statistics
These can all be applied to a series as well.
df.describe() | Summary statistics for numerical columns |
df.mean() | Return the mean of all columns |
df.corr() | Finds the correlation between columns in a DataFrame. |
df.count() | Counts the number of non-null values in each DataFrame column. |
df.max() | Finds the highest value in each column. |
df.min() | Finds the lowest value in each column. |
df.median() | Finds the median of each column. |
df.std() | Finds the standard deviation of each column. |
Download a printable version of this cheat sheet
If you'd like to download a printable version of this cheat sheet you can do so below.
This Pandas cheat sheet through the basics of Pandas that you will need to get started on wrangling your data with Python.
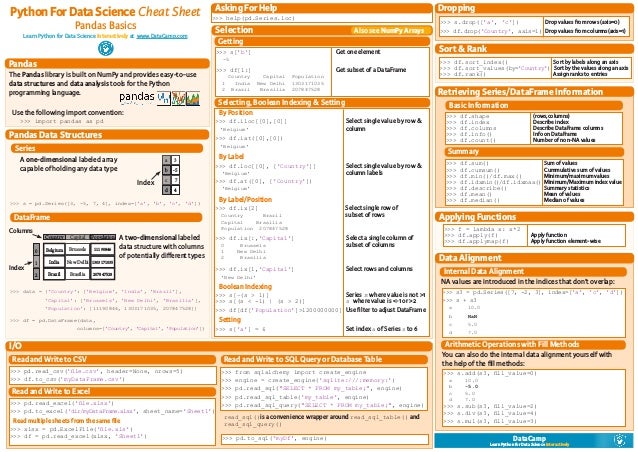
The Pandas cheat sheet will guide you through the basics of Pandas, going from the data structures to reading, writing, selection, dropping indices or columns, sorting and ranking, retrieving basic info of the data structures you're working with to applying functions and data alignment.
Importing Data
Pandas library offers a set of reader functions that can be performed on a wide range of file Pandas cheat sheet for importing data.
Exporting Data
list of write operations which are useful while writing data into a file – pandas cheat sheet for exporting data.
Viewing/Inspecting Data
Create Test Objects
Selection
Pandas Cheat Sheet Pdf
Selecting by position and selecting by label.
Data Cleaning
Sort, Filter and Group-by
Very useful feature offered by Pandas is the sorting of DataFrame – pandas cheat sheet for sorting, filtering & group by.
Pandas Python Cheat Sheet Pdf

pd.read_csv(filename) | From a CSV file |
pd.read_table(filename) | From a delimited text file (like TSV) |
pd.read_excel(filename) | From an Excel file |
pd.read_sql(query, connection_object) | Read from a SQL table/database |
pd.read_json(json_string) | Read from a JSON formatted string, URL or file. |
pd.read_html(url) | Parses an html URL, string or file and extracts tables to a list of dataframes |
pd.read_clipboard() | Takes the contents of your clipboard and passes it to read_table() |
pd.DataFrame(dict) | From a dict, keys for columns names, values for data as lists |
Exporting Data
df.to_csv(filename) | Write to a CSV file |
df.to_excel(filename) | Write to an Excel file |
df.to_sql(table_name, connection_object) | Write to a SQL table |
df.to_json(filename) | Write to a file in JSON format |
Create Test Objects
Useful for testing code segements
pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(20,5)) | 5 columns and 20 rows of random floats |
pd.Series(my_list) | Create a series from an iterable my_list |
df.index = pd.date_range('1900/1/30', periods=df.shape[0]) | Add a date index |
Viewing/Inspecting Data
df.head(n) | First n rows of the DataFrame |
df.tail(n) | Last n rows of the DataFrame |
df.shape() | Number of rows and columns |
df.info() | Index, Datatype and Memory information |
df.describe() | Summary statistics for numerical columns |
s.value_counts(dropna=False) | View unique values and counts |
df.apply(pd.Series.value_counts) | Unique values and counts for all columns |
Selection
df[col] | Return column with label col as Series |
df[[col1, col2]] | Return Columns as a new DataFrame |
s.iloc[0] | Selection by position |
s.loc['index_one'] | Selection by index |
df.iloc[0,:] | First row |
df.iloc[0,0] | First element of first column |
Data Cleaning
df.columns = ['a','b','c'] | Rename columns |
pd.isnull() | Checks for null Values, Returns Boolean Arrray |
pd.notnull() | Opposite of pd.isnull() |
df.dropna() | Drop all rows that contain null values |
df.dropna(axis=1) | Drop all columns that contain null values |
df.dropna(axis=1,thresh=n) | Drop all rows have have less than n non null values |
df.fillna(x) | Replace all null values with x |
s.fillna(s.mean()) | Replace all null values with the mean (mean can be replaced with almost any function from the statistics section) |
s.astype(float) | Convert the datatype of the series to float |
s.replace(1,'one') | Replace all values equal to 1 with 'one' |
s.replace([1,3],['one','three']) | Replace all 1 with 'one' and 3 with 'three' |
df.rename(columns=lambda x: x + 1) | Mass renaming of columns |
df.rename(columns={'old_name': 'new_ name'}) | Selective renaming |
df.set_index('column_one') | Change the index |
df.rename(index=lambda x: x + 1) | Mass renaming of index |
Filter, Sort & Groupby
df[df[col] > 0.5] | Rows where the col column is greater than 0.5 |
df[(df[col] > 0.5) & (1.7)] | Rows where 0.7 > col > 0.5 |
df.sort_values(col1) | Sort values by col1 in ascending order |
df.sort_values(col2,ascending=False) | Sort values by col2 in descending order |
df.sort_values([col1,ascending=[True,False]) | Sort values by col1 in ascending order then col2 in descending order |
df.groupby(col) | Return a groupby object for values from one column |
df.groupby([col1,col2]) | Return groupby object for values from multiple columns |
df.groupby(col1)[col2] | Return the mean of the values in col2, grouped by the values in col1 (mean can be replaced with almost any function from the statistics section) |
df.pivot_table(index=col1,values=[col2,col3],aggfunc=max) | Create a pivot table that groups by col1 and calculates the mean of col2 and col3 |
df.groupby(col1).agg(np.mean) | Find the average across all columns for every unique col1 group |
data.apply(np.mean) | Apply a function across each column |
data.apply(np.max,axis=1) | Apply a function across each row |
Join/Comine
df1.append(df2) | Add the rows in df1 to the end of df2 (columns should be identical) |
df.concat([df1, df2],axis=1) | Add the columns in df1 to the end of df2 (rows should be identical) |
df1.join(df2,on=col1,how='inner') | SQL-style join the columns in df1 with the columns on df2 where the rows for col have identical values. how can be one of 'left', 'right', 'outer', 'inner' |
Statistics
These can all be applied to a series as well.
df.describe() | Summary statistics for numerical columns |
df.mean() | Return the mean of all columns |
df.corr() | Finds the correlation between columns in a DataFrame. |
df.count() | Counts the number of non-null values in each DataFrame column. |
df.max() | Finds the highest value in each column. |
df.min() | Finds the lowest value in each column. |
df.median() | Finds the median of each column. |
df.std() | Finds the standard deviation of each column. |
Download a printable version of this cheat sheet
If you'd like to download a printable version of this cheat sheet you can do so below.
This Pandas cheat sheet through the basics of Pandas that you will need to get started on wrangling your data with Python.
The Pandas cheat sheet will guide you through the basics of Pandas, going from the data structures to reading, writing, selection, dropping indices or columns, sorting and ranking, retrieving basic info of the data structures you're working with to applying functions and data alignment.
Importing Data
Pandas library offers a set of reader functions that can be performed on a wide range of file Pandas cheat sheet for importing data.
Exporting Data
list of write operations which are useful while writing data into a file – pandas cheat sheet for exporting data.
Viewing/Inspecting Data
Create Test Objects
Selection
Pandas Cheat Sheet Pdf
Selecting by position and selecting by label.
Data Cleaning
Sort, Filter and Group-by
Very useful feature offered by Pandas is the sorting of DataFrame – pandas cheat sheet for sorting, filtering & group by.

